You can produce vegetables either by directly sowing seeds into the garden or by transplanting seedlings that have been prepared in pots beforehand. We recommend the direct-sowing method for horseradish, carrots, and other root crops as well as for spinach, Japanese mustard spinach, and other soft vegetables with short cultivation periods and the transplantation method for other crops due to management considerations.
Since the task of preparing seedlings can be troublesome and difficult for some vegetables, a novice might find it acceptable to purchase prepared potted seedlings from a lawn and garden supplies store.
There are three different methods of sowing seeds: stripe seeding, point seeding, and broadcast seeding. Choose the right method for you depending on the type of vegetable being grown and the location where the seeds are to be sown.
Stripe seeding is a method of seeding that is easy to control and widely used. It is ideal for spinach, Japanese mustard spinach, carrots, and more.
Point seeding is used for Japanese radish, corn, and certain other types of vegetables. Key to this method is the spacing that you should place between one seed and the next. This method makes it easier to thin out the crop if necessary.
Broadcast seeding is used for vegetables with a short growth period.
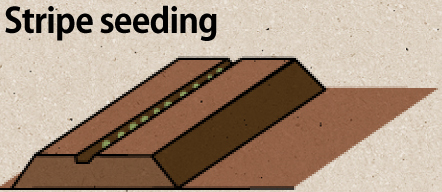
Create a seed furrow that is 0.5
to 1 centimeter deep and sow
your seeds in this furrow.

Establish a planting distance suitable for the vegetable to be cultivated and create seeding holes using a glass bottle at the selected positions.
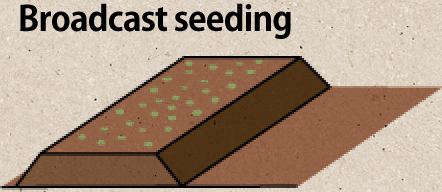
Disperse seeds evenly across the entire ridge and cultivate the resulting plants while thinning them as required.
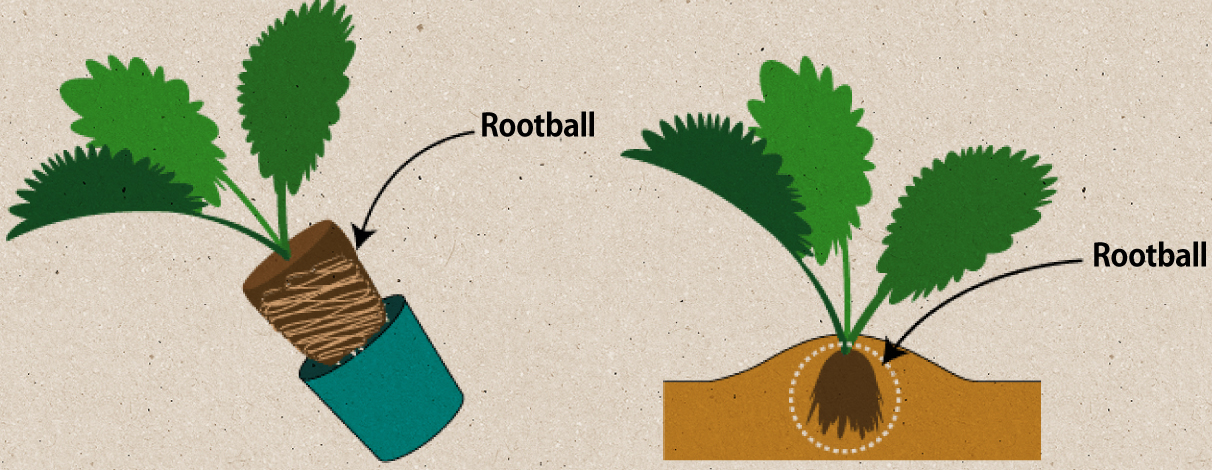
When transplanting a potted seedling, invert the pot, grip the seedling with your hand, and effortlessly remove the seedling from the pot without damaging the roots.
Insert a pinch of fast-acting fertilizer (chemical fertilizer or other such option) and mix it into the soil inside a prepared planting hole. Place the selected seedling on top of this mixed soil without causing its root clump to crumble and lose its form.
At this time, make adjustments so that the base of the plant is slightly elevated.
If the soil is dry, create a shallow ditch around the seedling after it has been planted and place water into this ditch.
Seedlings should ideally be planted on a cloudy, windless day.