If your soil is properly prepared, most vegetables can be grown regardless of slight environmental differences. Nevertheless, you will still need to think about how you select vegetables for the given conditions since suitability will depend on such factors as the size of the garden, sunlight exposure, and moisture (state of dryness).
At the end of the day, it is also simply more enjoyable to cultivate multiple vegetables for a homegrown vegetable garden.
Thus, you can enjoy harvesting vegetables year-round if you select your favorites from among typical vegetables that are relatively easy to raise and formulate a cultivation plan for each season.
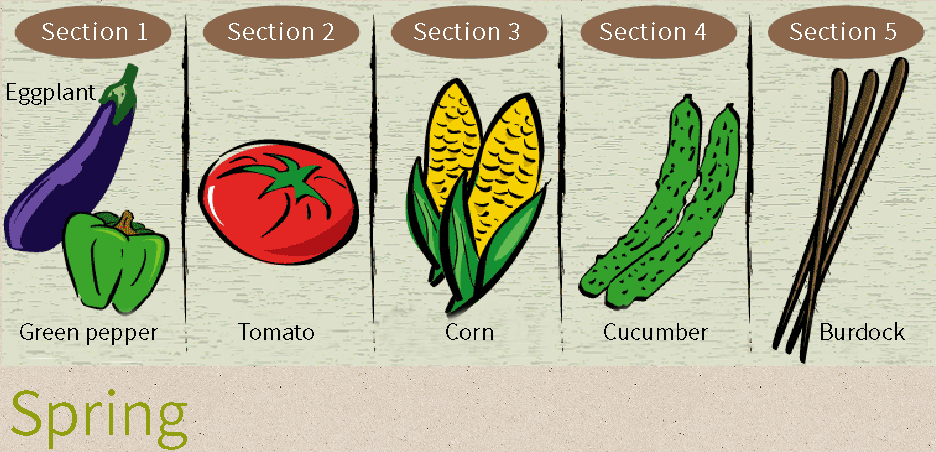
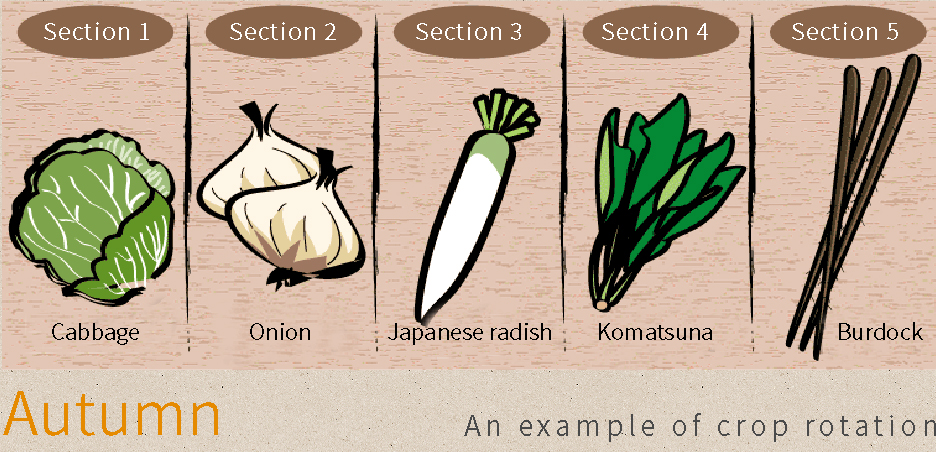
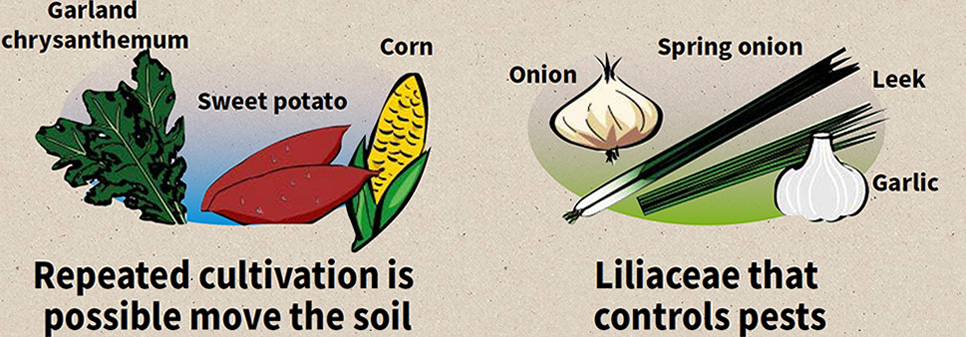
If you continuously plant the same vegetable crop in the same soil, you could give rise to repeated cultivation damage(*). Repeated cultivation should be avoided in particular for eggplants, tomatoes, green peppers, potatoes, and other vegetable plants belonging to the nightshade family as well as for taro, peas, fava beans, and more since these examples are especially susceptible to damage.
Rotating crops by cultivating different vegetables is effective for preventing repeated cultivation damage.
When formulating a cultivation plan, it is important to consider what crops will be grown and the locations in your garden where such crops will be grown and otherwise make efforts to avoid engaging in repeated cultivation.
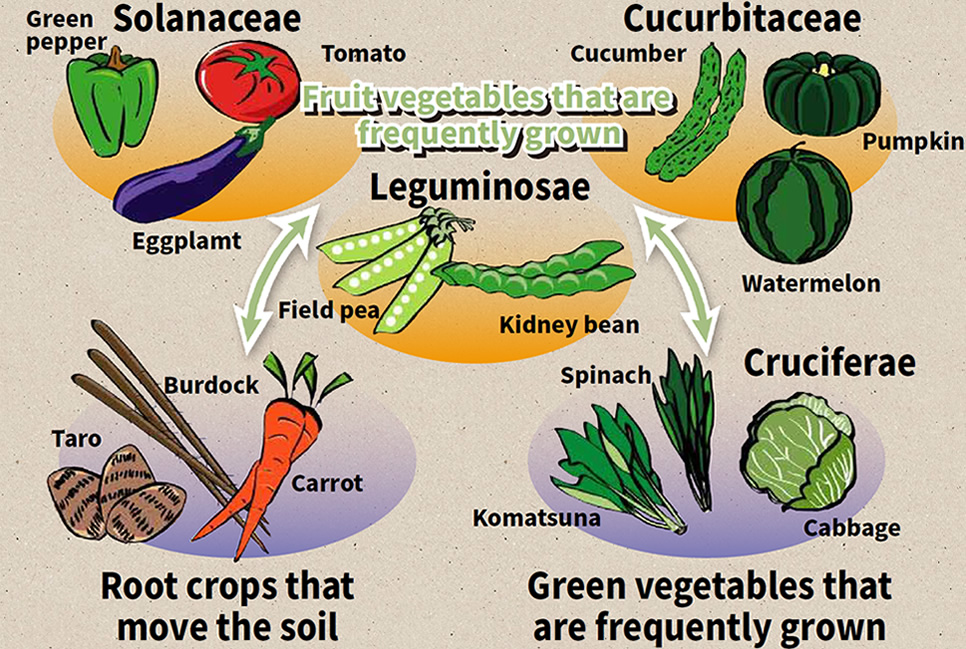
*Repeated cultivation damage: If you grow the same vegetable crop in the same location every year, pathogenic bacteria will proliferate and soil components will become skewed thereby resulting in worsening growth and development conditions with each passing year.